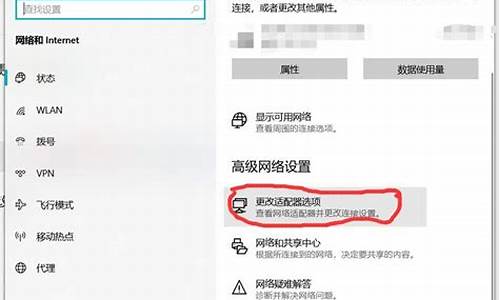
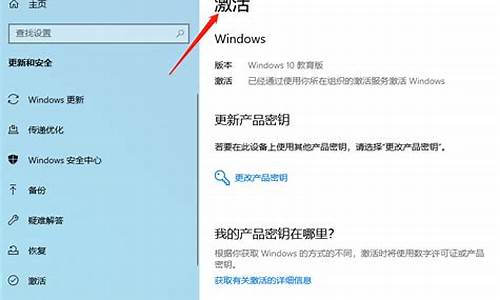
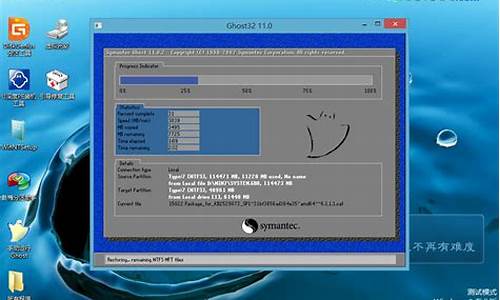
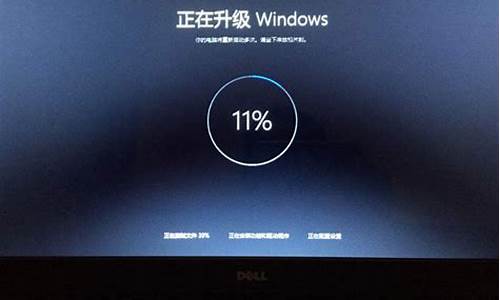
如何将系统装到d盘,电脑系统倒装

倒装式复合模是凸凹模装在下模座,和正装复合模相对。根据凸凹模在模具中的装配位置不同,分为正装复合模和倒装复合模两种。正装复合模:凸凹模装在上模座上的称为正装复合模。倒装复合模:凸凹模装在下模座上的称为倒装复合模。
倒装模具唧嘴在后模顶针顶出一侧,也就是说进胶和顶出是同一侧。工业生产上用以注塑、吹塑、挤出、压铸或锻压成型、冶炼、冲压等方法得到所需产品的各种模子和工具。 简而言之,模具是用来成型物品的工具,这种工具由各种零件构成,不同的模具由不同的零件构成。
主要通过所成型材料物理状态的改变来实现物品外形的加工。素有“工业之母”的称号。在外力作用下使坯料成为有特定形状和尺寸的制件的工具。广泛用于冲裁、模锻、冷镦、挤压、粉末冶金件压制、压力铸造,以及工程塑料、橡胶、陶瓷等制品的压塑或注塑的成形加工中。
扩展资料大水口模具:流道及浇口在分模线上,与产品在开模时一起脱模,设计最简单,容易加工,成本较低,所以较多人采用大水口系统作业。塑料模具结构分为两部分:动模和定模。随注射机活动部分为动模,在注射机射出端一般不活动称为定模。
细水口模具:流道及浇口不在分模线上,一般直接在产品上,所以要设计多一组水口分模线,设计较为复杂,加工较困难,一般要视产品要求而选用细水口统。细水口模具的定模部分一般由三块钢板组成故也有称此类结构模具为“三板模”。三板模是细水口模具中最简单的结构。
热流道模具:此类模具结构与细水口大体相同,其最大区别是流道处于一个或多个有恒温的热流道板及热唧嘴里,无冷料脱模,流道及浇口直接在产品上,所以流道不需要脱模,此系统又称为无水口系统,可节省原材料,适用于原材料较贵、制品要求较高的情况,设计及加工困难。
模具成本高。 热流道系统,又称热浇道系统,主要由热浇口套,热浇道板,温控电箱构成。我们常见的热流道系统有单点热浇口和多点热浇口二种形式。
单点热浇口是用单一热浇口套直接把熔融塑料射入型腔,它适用单一腔单一浇口的塑料模具;多点热浇口是通过热浇道板把熔融料分枝到各分热浇口套中再进入到型腔,它适用于单腔多点入料或多腔模具。
百度百科-模具
倒装句在中学英语教材中反复出现? 本文就中学生应掌握的有关倒装句的知识作了比较系统的归纳?
希望同学们能系统地掌握这方面的知识。
一般来说,倒装分为全部倒装和部分倒装。有的倒装是因为语法需要而出现的,有的倒装则是因为结构平衡的需要而出现的。
一、全部倒装
1.以here, there, now,
then开头的句子,谓语动词要放在句子的主语之前。这种句子中的谓语动词通常是不及物动词。如:
Here comes the train!
There goes the bell!
注意:如果句子的主语是人称代词,则不能使用倒装结构。如:
Here it comes! / There it goes!
2.有些动词短语以副词out,in,up,down,away等结尾,构成不及物动词短语。这时,为了使句子更形象,常将这些副词提前到句首。这时,句中的谓语动词要放在句子主语的前面,构成全部倒装。(注意,这时句子的主语也必须是名词。如果是人称代词,也不能使用倒装结构。)如:
Up went the rocket.
Up it went.
3.为了强调表示地点的介词短语,常将这个介词短语放在句首,构成全部倒装。注意,这时句子的谓语动词通常是不及物动词。如:
In the front of the lecture hall sat the speaker.
4.表语置于句首,且主语较长或结构较复杂的句子要用全部倒装。如:
Gone are the days when we had nothing to eat.
5.so/neither/nor表示前面所说的情况也适合于后者,其倒装结构为“so/neither/nor+助动词/系动词/情态动词+主语”(so表示肯定意义,neither/nor表示否定意义)。如:
She has finished her homework,so has her brother.
She hasn’t gone there, neither/nor has he.
但如果so表示强调, 即强调前面所说的情况的真实性时,
其结构是“so+主语+助动词/系动词/情态动词”,这里的主语同前一个句子的主语指的是同一人或物。如:
She knows little English,so she does. 她英语懂得不多。她的确如此。
二.部分倒装
1.用于疑问句中。如:
How did you do that?
Did you see the film yesterday?
2.用于省略if的虚拟条件状语从句中。如果我们将连词if省略,应把were, had,
should提到主语前面。如:
If you had come yesterday, you would have seen him.
→Had you come yesterday, you would have seen him.
3.用于as引导的让步状语从句中。as引导的让步状语从句引起的倒装有以下几种形式:
1) 副词置于句首。如:
Much as I like it (=Although I like it very much), I
will not buy it.
2) 动词原形置于句首。如?
Wait as you may(=Although you may wait), he will not
see you.
3) 形容词或名词置于句首。如:
Proud as the nobles are (=Although the nobles are
proud), they are afraid to see me.
Child as he is (=Although he is a child), he can
tell right from wrong.
注意:如果名词前有形容词修饰时,as 引导的倒装句中要保留不定冠词。如:
A bad-tempered man as he is (=Although he is a
bad-tempered man), he loves me deeply.
4.具有否定意义的副词或连词(not,hardly,no sooner, not until,
seldom,not once,at no time,never,little等) 置于句首时,
句子(主句)采用部分倒装。如:
Little do we know about him.
No sooner had he closed his eyes than he fell
asleep.
Seldom does he come back on Sundays.
Not until he came back did I know about it.
5.only修饰句子的状语(从句)位于句首时,句子(主句)要用部分倒装。如:
Only then did I realize the importance of English.
Only when a child grows up does he understand his
parents’ intentions.
但如果only修饰的是句子的其它成分,则无需倒装。如:
Only socialism can save China.
(only修饰的是句子的主语,故仍用正常语序。)
6.not only…but also… 连接两个并列分句时,第一个分句应使用部分倒装。如:
Not only does he do well in his lessons, but also he
often helps others with their lessons.
7.so…that结构中的倒装。有时要强调so所修饰的形容词或副词,常将so
连同它所修饰的形容词或副词一起提到句首。这时,主句要用倒装结构。如:
He runs so fast that he is far ahead of others.
→So fast does he run that he is far ahead of others.
He is so clever that he can work out all the
difficult problems in the book.
→So clever is he that he can work out all the
difficult problems in the book. (全部倒装)
当主语在谓语前出现时叫顺序(the natural order)。在某些情况下,我们可以把谓语成分放在主语前面,这种词序叫做倒装( the inverted order)。
倒装分两种:配合语法条例的倒装,叫“grammatical inversion”;配合强调语势的叫“emphatic inversion”。
语法上的倒装句是强制性的,包括下列 7 种:
⒈疑问句,如:
● Can you do it?
● How old are you?
● When did you know him?
● Why did you elect him as captain?
● Which of these apples do you prefer?
但疑问代词做主语时,不必倒置,如:
● Who is your English teacher?
● What happened last night?
⒉表示“愿望”的句子,如:
● May God bless you.
● Long live the king!
⒊“There”引导的句子,如:
● There are many cars on the road.
● There stand some big trees near the river.
● There is a security guard outside the bank.
⒋感叹句,如:
● How beautiful the flower is!
● What a smart boy you are!
⒌有连接词“so, neither, nor”的句子,如:
● Tom can ride a bicycle; so can I.
● She can't sing; neither can he.
● John has never been late; nor have I.
⒍省略连词“if”的条件副词分句,如:
● Were I you, I would not do such a thing.
● Should the machine break down again, send it back to us.
● Had you worked harder, you would have passed.
⒎“as, however”连接的让步副词分句,如:
● Small as the pen is, it is a powerful weapon.
● However busy you are, you should spend some time reading Zaobao weekly.
谈过了语法上的倒装句,现在谈强调的倒装句。
● Never have I seen such a wicked man.
● On no account must this employee be removed.
● Not until he told me had I heard anything of it.
● No sooner had I left than the rain came.
● Up jumped the puppy.
● In came John.
● Down fell the rotten branches from the tree.
● Out came a woman and her maid.
304929024
声明:本站所有文章资源内容,如无特殊说明或标注,均为采集网络资源。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。